Bottom Line
The Bank of Canada is no doubt delighted that inflation continues to cool. The Bank expects price gains to reach 3% by midyear and return to near their 2% target by the end of 2024. But they said getting the prices back to 2% could prove more difficult because inflation expectations are coming down slowly, and service prices and wage growth remain elevated.
Governor Tiff Macklem, speaking at the IMF and World Bank meetings in Washington recently, said the Bank of Canada is prepared to end quantitative tightening earlier than planned if the economy needs stimulation. Quantitative tightening is the selling of government bonds on the Bank's balance sheet, which takes money out of the economy.
Macklem said his officials discussed hiking rates further during deliberations for the April 12th decision to continue to pause and reiterated that "it is far too early to be thinking about cutting interest rates."
His comments provide a glimpse into the Bank of Canada's strategy for shrinking its balance sheet, which ballooned to more than $570 billion during the pandemic as it bought large quantities of government bonds — to restore market functioning during the initial Covid shock and then to provide a stimulus for the economy.
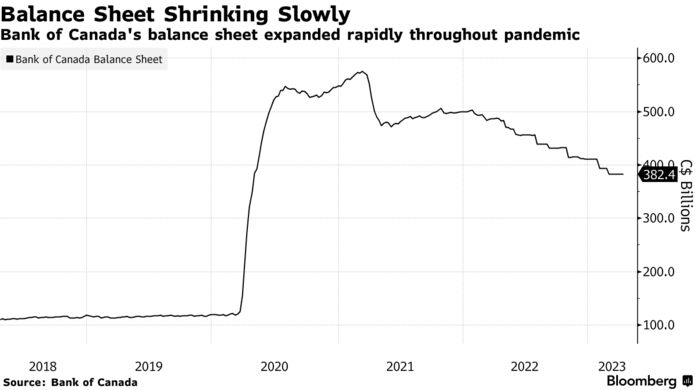
The remarks show an acknowledgment among policymakers that their plans could shift if there's a negative economic shock that requires a loosening of monetary policy.
According to Bloomberg News, swaps traders are now betting the Bank of Canada's next move will be a cut later this year. The governor pushed back on those expectations in a press conference this week. He and his officials discussed the possibility that rates need "to remain restrictive for longer to get inflation all the way back to target."
In a speech last month, Deputy Governor Toni Gravelle said quantitative tightening will likely end in late 2024 or early 2025. That marked the first time the Bank of Canada put a date on abandoning the program.
|